World & US Energy News
Just one day in the life of energy news on the planet
World & US Energy News
Just one day in the life of energy news on the planet
World & US Energy News
is written by
columnist
George Harvey

Mid November 2016
Science and Technology:

¶ The top US negotiator told a packed COP22 news briefing that the passion and dedication displayed in the effort to deliver the Paris treaty was strong enough to withstand whatever impacts may come of a Trump presidency. He said, however, that he had no news on who might lead on climate change issues in a Trump administration. [BBC]
¶ Businesses reported $14 billion of losses in 2015 due to water scarcity, droughts, and tightening environmental regulations, a report released at the climate summit in Marrakech said. Of over 1,200 of the largest listed companies exposed to water risk, just about half responded, so the loss figure is clearly underreported badly. [The Guardian]
¶ Civil societies from across the globe converged at the UN’s COP22 conference, demanding that world leaders halt fossil fuel extraction and make an urgent just transition to a clean energy future to slow climate change. Experts say the reductions needed to limit warming to 1.5° C will require more reductions than have been pledged. [NorthEast Today]
World:
¶ It took “one of the most significant severe thunderstorm outbreaks in recent decades”, with seven tornadoes and wind speeds of 260 km/h (160 mph), to cause last September’s severe blackout in South Australia. Conservatives were quick to blame renewable energy, but it’s now clear that the entire network was at risk. [Gizmodo Australia]
¶ Atlantis, a global leader in the tidal power sector, announced that first power has been produced from the MeyGen project site in the Pentland Firth, Scotland. The turbine, supplied by Andritz Hydro Hammerfest, has been successfully installed and plugged into the pre-laid cable that connects it to the electric power grid. [Your Renewable News]
¶ A full 30% of the world’s electricity generation comes under the umbrella of just nine energy companies. They have just joined forces to ramp up technology investments for decarbonization. The global effort was announced by the companies’ nonprofit organization, the Global Sustainable Electricity Partnership. [Triple Pundit]
¶ The UK produced more than 50% of its electricity from low-carbon sources in the third quarter of 2016, a new report from Imperial College London and power firm Drax said. For the quarter, the contribution of nuclear, biomass, hydro, wind, solar and low-carbon electricity imports from France stood at 50.2%. [Bioenergy Insight Magazine]
¶ ExxonMobil’s Production Vice President said Norway should provide companies with fiscal incentives to continue producing at declining oil fields in the North Sea, to offset falling private investment funding. ExxonMobil seems to be requesting that the Norwegian government give tax incentives to some very wealthy oil corporations. [CleanTechnica]
US:
¶ President-elect Trump has pledged to boost the oil and gas sector and bring back coal, reversing President Obama’s efforts to encourage renewable energy and cut dependence on fossil fuels. But analysts say Trump’s policies could serve to worsen the global energy glut, reducing prices and doing little to save “Big Coal.” [Channel NewsAsia]
¶ Microsoft said its Cheyenne data center in Wyoming will now be powered entirely by 237 MW of wind energy. The company is buying 178 MW from the Bloom Wind Project in Kansas to help bring this new project online, along with an additional 59 MW from the Happy Jack and Silver Sage wind farms in Wyoming. [News18]
Wind turbines and buffalo
(Photo by CGP Grey, CC BY SA, Wikimedia Commons)
¶ In Vermont, the $80 million Searsburg wind project is now under way. The project will have 15 wind turbines, which will produce enough energy to power about 14,000 average Vermont households. It is expected to deliver at least $400,000 per year in local economic benefits and $300,000 per year for the state of Vermont. [Construction Equipment Guide]
¶ The dozens of buildings on the campus of St Olaf College, in Northfield, Minnesota, are now being powered entirely by wind energy, the liberal arts school and Xcel Energy announced. By choosing Xcel’s Windsource program for its electrical service, St Olaf has become the largest Windsource customer in the state. [Minneapolis Star Tribune]
¶ Microsoft, Walmart, Best Buy, Ikea, Staples, and Mars Inc are among a group of eighteen major corporations that have sent a letter to Virginia lawmakers and the Virginia State Corporation Commission calling for “an explicit legal framework” to expand access to renewable energy from utilities and third-party sellers. [Richmond.com]
¶ Four decades after construction began at the Bellefonte nuclear plant, Nuclear Development LLC offered to buy the unfinished plant from the Tennessee Valley Authority for $111 million. The company plans to invest up to $13 billion to complete the plant. Nuclear plants are struggling, however, and five have closed in five years. [BloombergQuint]
Mid July 2016
World:

Clear-cut forest. Illustrated photo by Calibas. CC BY-SA 3.0. Wikimedia Commons.
¶ The Scottish courts have quashed planning consent for 2.3 GW of offshore wind farms off the country’s east coast. In doing so, it sided with claims by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, which was acting to protect birds and other wildlife. The Scottish Government said it remains committed to offshore wind. [reNews]
¶ Japan’s SoftBank Group Corp signed a pact with Korea Electric Power Corp and Mongolian investment company Newcom LLC to co-develop and co-invest in Mongolian renewable energy projects. The memorandum of understanding calls for work on wind and solar PV projects at the city of Ulaanbaatar. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ A newly elected local governor will ask Kyushu Electric Power Co for a temporary shutdown of Sendai nuclear plant, Japan’s only operating facility, as early as August. He has said he wants the shutdown for checks on the impact of a series of strong quakes that struck neighbouring Kumamoto earlier this year. [Himalayan Times]
¶ Nigus Greenergy and Volt Renewables have signed a memorandum of understanding relating to 300 MW of solar PV plants to be developed and commissioned in Nigeria next year. The project will comprise three, 100 MW solar plants located in northern Nigeria and will be 10% of Nigeria’s generating capacity. [pv magazine]
US:
¶ As it is coming together, the Democratic National Convention platform takes on climate change as one of the most urgent issues of our day. The platform supports a price on carbon and methane emissions. It takes a tough stance on fossil fuel companies, calling for eliminating tax breaks and subsidies for these firms. [Triple Pundit]
¶ The final Republican platform would pull the United States out of the international climate accord, open national forests for logging, and declare coal a “clean energy resource.” It would also end limits to CO2 emissions, pull the US out of the United Nations climate process, and end all subsidies to renewable energy. [Deutsche Welle]
¶ Discount Power, a licensed retail energy supplier, announced they have launched green energy products for their customers to support clean energy production and reduce use of fossil fuels. They are offering 100% wind energy for homes and businesses in Connecticut, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, Ohio, and Maryland. [Power Online]
¶ The Obama Administration announced it has partnered with six federal agencies to pursue a new catalytic goal to deploy 1 GW of solar power systems for low-to-moderate-income families by 2020. The new objective is a tenfold increase of the president’s initial target of 100 MW set in his Climate Action Plan. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ The Vermont Public Service Board issued an order scaling back support for solar, bringing loud complaints from environmentalists and industry officials. The changes include a sharp reduction in the amount of power utilities will be required to buy from customers who generate their own power for net metering. [Barre Montpelier Times Argus]
¶ The Montana Public Service Commission voted to establish contract terms and conditions between Greycliff Wind Prime and NorthWestern Energy, for a 25-MW wind farm. Under federal law, Northwestern Energy must purchase the power at the utility’s “avoided cost,” the cost if would have incurred buying elsewhere. [kmmsam]
Early March 2016

¶ South Africa will connect 7,000 MW of renewable power to its grid by the middle of this year, when the first 47 projects become fully operational, the energy minister said. Africa’s most industrialised country has turned to solar and wind power to plug electricity shortages. [Yahoo News]
*CAPTION — Illustrated is The Fort Calhoun Nuclear Plant which flooded in 2011. Army Corps of Engineers photo. Public domain. Wikimedia Commons. Read more below
¶ The UK Energy Bill, which provides for the closure of the Renewables Obligation support regime for new onshore wind in Great Britain, concluded its passage through Parliament. Industry body RenewableUK called for tapping into onshore wind as the cheapest power option. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ Japan’s government is in the process of building a new fleet of coal-fired power stations that could prove worthless in a few decades as a result of overcapacity and falling energy costs, potentially stranding ¥6,223 billion ($56 billion) of assets, according to a new study. [Business Green]
¶ China’s largest coal company, Shenhua Energy, has signed an agreement with SolarReserve to build the largest amount of completely dispatchable solar electricity in the world: 1 GW of concentrating solar power (CSP). Shenhua will be responsible for the power block side. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Tasmania has returned to 100% renewable electricity, at least temporarily, as significant rainfalls replenished dam levels and the state was able to operate without gas-fired or diesel generation for the first time since the Basslink cable was cut, preventing power imports from Victoria. [RenewEconomy]
¶ Northland Power Inc said it has installed 50 turbines at the 600-MW Gemini offshore wind farm and reported results for the first quarter of 2016. Of these, 27 are already producing power, bringing pre-completion revenues. Completion is expected in the middle of next year. [SeeNews Renewables]
¶ Outdoor air pollution has grown 8% globally in the past five years, with billions of people around the world now exposed to dangerous air, according to new data from more than 3,000 cities compiled by the World Health Organisation. The problem extends worldwide. [The Guardian]
US:
¶ Thousands of oil and gas industry wastewater spills in North Dakota have caused “widespread” contamination from radioactive materials, heavy metals and corrosive salts, putting the health of people and wildlife at risk, researchers from Duke University said in a peer-reviewed study. [DeSmogBlog]
North Dakota, Williston – Bakken – Oil and Gas – Missouri River. Photo Credit: EcoFlight.
¶ The coal industry has been counting on exports to fill the gap in its declining sales, but it looks like the US Army Corps of Engineers has put the damper on that, at least for now. USACE suspended the permitting process for a proposed new coal export terminal in Washington State. [CleanTechnica]
¶ New Jersey’s largest electric utility wants to dramatically step up the number of ratepayer-supported solar projects it installs on landfills and brownfields. Public Service Electric & Gas Co asked state regulators to allow it to spend $275 million to install 100 MW of solar panels. [Philly.com]
¶ Nothing is changing the corporate climate more than climate change. And what state is putting the topic on the front burner? New York, which is motivated by a progressive governor and memories of a 2012 superstorm, and his program, Reforming Energy Vision (REV). [Environmental Leader]
¶ The Fort Calhoun Nuclear Station survived a fire, a flood and the close scrutiny of federal regulators. But it may be no match for the market. Omaha Public Power District executives are making recommendations to the board, one of which is to close the plant, as it is too costly to run. [KETV Omaha]
¶ Foes of a third nuclear reactor at Dominion Virginia Power’s North Anna Power Station, near Mineral, Virginia, have taken their case to the shareholders of parent company Dominion Resources, which is holding its annual shareholders meeting in Columbia, South Carolina. [Bacon’s Rebellion]
¶ This summer, if all goes according to plan, the second reactor at Watts Bar Nuclear Power Plant, in Spring City, Tennessee, will begin supplying power to the US electrical grid. Construction on the reactor has proceeded with repeated delays since the project began. That was 43 years ago. [Quartz]
Early February 2016
World:
¶ An article in the journal Nature Energy discusses the fact that renewable electricity investment has now outstripped spending on fossil fuels and that policies are focusing on improving energy efficiency and energy systems flexibility. It says these point to a global momentum toward sustainable energy systems. [CleanTechnica]

¶ The UK’s Department of Energy & Climate Change published its latest update on the country’s greenhouse gas emissions levels. According to the figures, UK’s greenhouse gas emissions were estimated to be at 514.4 million tonnes carbon dioxide equivalent in 2014, or around 35% lower than 1990 levels. [CleanTechnica]
¶ A Greenpeace Southeast Asia report revealed the health impacts of coal-fired power plant in the Philippines. It says 960 people die there each year due to stroke, ischemic heart disease, other cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory diseases. With proposed new plants, that figure could more than double. [eco-business.com]
¶ King Mohammed VI of Morocco inaugurated his country’s first solar power plant, a massive project that the country sees as part of its goal of boosting its clean energy output. Pakistan’s Prime Minister Abdelilah Benkirane and French Environment Minister Segolene Royal were among those who attended. [The Express Tribune]
¶ As of last month, three school divisions in Peace Country, an area of western Canadian, are powered by wind energy. The school divisions announced that their schools and administration offices now get power from a wind facility near Provost, about three hours southeast of Edmonton. [Alberta Daily Herald Tribune]
¶ India has decided to join a global treaty on nuclear accident liability. The country ratified the Convention on Supplementary Compensation for Nuclear Damage. This is the latest effort the government has taken to ease suppliers’ concerns that they would be open to liability claims in case of a nuclear accident. [Bloomberg]
US:
¶ In a stunning trend with broad implications, the economy has grown significantly since 2007, while electricity consumption has been flat, and total energy demand dropped. The economy has grown 10% since 2007, while primary energy consumption has fallen by 2.4%, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance. [ThinkProgress]
¶ Natural gas-fired power projects continue to be developed in the Electric Reliability Council of Texas footprint, but low prices and the prospect of more renewable capacity has some wondering how many new gas-fired units will actually come online over the next few years. [Hellenic Shipping News Worldwide]
¶ The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has published a report with some fascinating points about renewable energy in the Salton Sea area. It covers potentials for developing solar, geothermal, and algal energy sources. There is also a great potential for extracting lithium from brine. [CleanTechnica]
Salton Sea. Released into the public domain (by the author). Wikimedia Commons.
¶ County prosecutors filed a criminal misdemeanor charge against Southern California Gas Co. According to the District Attorney’s Office, SoCalGas is being charged because they allegedly failed to report the leak at Porter Ranch immediately. Meanwhile, the company now also faces a wrongful death lawsuit. [Lawyer Herald]
¶ The world’s largest manufacturer of office furniture will soon offset 70% of its total US electricity usage from wind power with a long-term virtual power purchase agreement. Steelcase, based in Grand Rapids, Michigan, just announced an agreement with Apex Clean Energy for 25 MW of wind power. [RMI]
Photo courtesy of Eric Ward via Flickr, Creative Commons license (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0).
¶ According to data just released in the 2016 Sustainable Energy in America Factbook – a project of Bloomberg New Energy Finance, produced for the Business Council for Sustainable Energy – the shift to renewables may be happening a lot faster than the EPA thought that it would less than a year ago. [HeraldNet]
January 2016

Caption: Contractors work on solar panels at the Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in Golden, Colorado.
Opinion:
¶ Why Renewable Energy is Defying Gravity • In the face of the lowest oil prices for over a decade, a record $329 billion was invested in clean energy worldwide in 2015. That seems counterintuitive: conventional wisdom says that cheap fossil fuels inhibit the growth of renewables. [MIT Technology Review]
¶ Oil is Dead and Renewable Energy is Killing It • Mark down 2015 and 2016 as special years. These two years might end up being two of the most important in the history of humankind. You might not see it yet, and that’s OK. It’s pretty easy to get preoccupied with everything else going on right now. [Money Morning Australia]
World:
¶ The Venezuelan government announced a 60-day economic emergency to deal with a crisis brought on by the huge fall in oil prices in the past 18 months, which slashed its revenues by 60%. The country has the world’s biggest known oil reserves, and oil exports account for as much as 95% of its revenue. [BBC]
¶ In a piece published on its website this week, the UK Solar Trade Association made it clear it believes that residential solar remains a good investment for householders, despite Government’s backsliding on their green policies, and in the wake of the recent modifications to the country’s Feed-in Tariff. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Gamesa announced it had received an unusual order for the supply and installation of 48 MW of special wind turbines. Gamesa will purpose-build 24 of its 2-MW wind turbines specifically configured to withstand the low temperatures and low air density conditions 3,400 meters (11,155 feet) above sea level. [CleanTechnica]
¶ India’s installed capacity of solar PVs has crossed the 5,000 MW milestone. The Indian Government has a target of 100 GW of PV capacity by the year 2021-22. It envisages 60 GW of ground mounted grid-connected solar power and 40 GW through roof-top grid interactive solar power. [Business Standard]
¶ Carbon dioxide emissions have declined by 22.72 lakh tonnes (3 million tons) in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh due to the generation of power from renewable energy sources, a senior official said. The state is promoting alternative energy, including wind, solar, biomass, and minor hydro projects. [Business Standard]
US:
¶ The Obama administration announced on Friday that it will suspend new coal leasing on federal lands and overhaul the program to better reflect environmental costs. This could be a turning point in climate policy. It is a concrete measure toward leaving fossil fuels in the ground, as the science demands. [InsideClimate News]
¶ The city of Philadelphia dropped an interesting wrinkle into the building code that took effect on January 1. All new residential construction must have in-sink garbage disposals. The garbage will go to the city’s sewage treatment bio-digesters, where it will produce methane to power electric generation. [Metro.us]
¶ Lewis County, New York, reached a final agreement on a solar project expected to offer the county and its municipal hospital significant cost savings. The county and Lewis County General Hospital are guaranteed a saving of at least $3.3 million over the contract’s 20-year term. [WatertownDailyTimes.com]
¶ Four months after it began work on a pair of solar farms near the Lowndes County Industrial Park, Silicon Ranch Corporation announced it is generating electricity. According to the company, the two facilities can generate 1.6 megawatts of electricity, enough to power more than 200 homes. [The Commercial Dispatch]
Silicon Ranch Corporation announced it is generating electricity at two solar farms near the Lowndes County Industrial Park. Courtesy photo
¶ A new grid modernization blueprint released by the US DOE seeks to integrate conventional and renewable power sources with energy storage and efficiency, while ensuring the grid is resilient against cyberattacks and climate change threats. Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz announced the plan. [POWER magazine]
¶ Enel Green Power has begun constructing its new 108-MW Drift Sand wind project, located in Grady County, Oklahoma. The wind farm is expected to be completed and enter into service by year’s end. According to EGP, construction requires an investment of about $180 million. [North American Windpower]
Sunset Turbines in Oklahoma, by US Geological Survey.
Licensed under Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons
¶ Placing a cost on carbon could have significant impacts for utility shareholders and open up power companies to new litigation risks, according to a new paper published in the journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. The paper quantified the potential liabilities of the top 10 emitters. [Utility Dive]
¶ Entergy Nuclear Operations Inc, which owns and operates the nuclear power plant, filed suit against Secretary of State Cesar Perales in federal court Thursday, seeking a court order to toss out the state’s refusal to grant the power plant a certificate to operate on the Hudson River.
[The Journal News | LoHud.com]
December 2015 and news from COP21 in Paris

Shanghai boom and gloom. Author Peter Dowley. CC BY-SA 2.0. Wikimedia Commons.
COP21:
¶ If coal is good for humanity, then someone has forgotten to tell the world’s poorest countries. In a strongly worded statement that came out on the first day of talks at COP21, the leaders of 30 of the world’s poorest countries said they wanted the world to be 100% renewable by 2050. [CleanTechnica]
¶ One event in Paris, a Climate Summit for Local Leaders will commit 1000 mayors and local leaders to “support ambitious long-term climate goals such as a transition to 100% renewable energy in our communities, or a 80% greenhouse gas emissions reduction by 2050”. [Blue & Green Tomorrow]
¶ As governments continue negotiations to hammer out a global climate deal at COP21, institutional investors assemble to highlight their contributions, reinforcing calls for robust Paris climate agreement to enable rapid scale up of investment in low-carbon transition. [Blue & Green Tomorrow]
¶ A senior Indian negotiator says his country will cut back its use of coal, if it gets sufficient cash from a Paris deal. The country believes rich nations responsible for the bulk greenhouse gas emissions released so far must provide cash if they want developing countries to cut their emissions. [TV Newsroom]
World:
¶ With nearly 3.1 GW of offshore wind capacity connections expected for 2015, Europe is driving the industry’s expected 3.6 GW of new capacity. Analysis from MAKE Consulting concludes that 2015 is likely to see 3.6 GW of new offshore wind capacity connected to local European grids. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The launch of the Carbon Pricing Leadership Coalition was the first time in UN climate talk history that heads of state have agreed to sit at same table as the leadership of nongovernment agencies and businesses to decide how to deploy carbon-pricing solutions across the world by 2020. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Google’s current renewable energy portfolio, worth approximately $3 billion, makes it one of the largest renewable energy owning utilities in the world. Google has invested in an array of renewable energy companies and runs several locations on hundreds of megawatts of clean energy. [Huffington Post]
¶ Norwegian oil and gas company Statoil has made the final investment decision to build the 30-MW Hywind floating wind farm offshore Peterhead in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The developer has tapped Siemens to supply five of its SWT-6.0-154 direct-drive offshore wind turbines for the project. [North American Windpower]
¶ A study released by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis showed that worldwide coal consumption is likely to decline between 2% and 4% in 2015, despite near decade-low coal prices. That’s on top of a 0.7% decline a BP study said happened in 2014. [Audubon Magazine Blog]
¶ In an announcement made at the United Nations Conference on Climate Change in Paris, Monsanto will stand trial for ecocide and crimes against humanity and nature at the International Court of Justice. An umbrella group of over 800 organizations in 100 countries is involved in the action. [Care2.com]
US:
¶ The United States deployed 60.3 MW of energy storage during the third quarter of the year, bringing the year’s cumulative total up over 100 MW. The figures come by way of GTM Research’s US Energy Storage Monitor, and represent a 46% increase from the second quarter of 2015. [CleanTechnica]
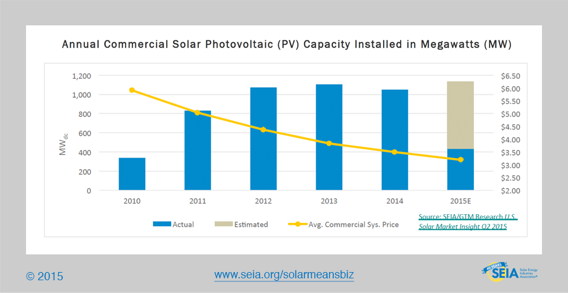
¶ According to a new study released earlier this week by the US Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), growth in the use of solar energy among America’s top companies has skyrocketed 183% over the last four years since the first Solar Means Business report was published. [CleanTechnica]
¶ While 150 world leaders are negotiating a climate deal in Paris, nine Northeastern states in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative are sharing $115 million from the latest auction under a regional pact that limits power plant emissions while supporting renewable energy and efficiency projects. [Rutland Herald]
¶ Vermont’s largest electric utility is getting ready to offer customers in-home batteries made by Tesla, best known for making electric cars. In a letter Thursday to the Public Service Board, Green Mountain Power said it would become the first US utility to offer the Tesla Powerwall. [Idaho Statesman]
¶ Scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographics Institution have found signs of nuclear contamination from Fukushima at an increased number of sites off the US West Coast, including the highest detected level to date from a sample collected about 1,600 miles west of San Francisco. [ObserverVoice.com]
Mid November 2015
Europe:
¶ The north of England is set to be home to Europe’s largest floating solar power system. Water company United Utilities is developing a 12,000 panel system covering an area of more than 45,000 square meters. It will cover about 33% of their electricity needs. The system will be on Godley reservoir in Hyde, Greater Manchester. [CNBC]
¶ The carbon content of electricity generation in Ireland fell to a record low last year, according to new figures by the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland. The country avoided 2.6 million tonnes of CO2 emissions in 2014. SEAI said without renewables, power generation emissions would have been around 23% higher. [Energy Voice]
¶ The UK’s Overseas Development Institute (ODI) and campaign group Oil Change worldwide (OCI) have now published a detailed analysis of G20 subsidies to oil, gas and coal production. The G20 countries spent around four times as much to prop up fossil fuel production as they did to subsidize renewable energy. [Financial Company Voices]
¶ In the UK, production subsidies of £5.9 billion have already benefited major fossil fuel companies operating in the country, most foreign-owned, while £3.7 billion is used to subsidise fossil fuel production overseas in countries including Russia, Saudi Arabia and China, the new analysis from the ODI and OCI found. [The Guardian]
¶ The Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland announced a Memorandum of Understanding with Apple to promote the development of ocean energy. Apple has committed a €1 million fund to help developers who receive SEAI grants to test their ocean energy prototypes in the Galway Bay Ocean Energy Test Site. [Your Renewable News]
¶ The cabinet of Angela Merkel’s ruling coalition has endorsed changes to the German electricity market, ensuring their passage into law. The law relies on market mechanisms to foster competition between electricity generation and flexibility options, rejecting generator proposals for an American-style capacity market. [POWER magazine]
US:
¶ More than 7,100 solar panels will provide power to areas of Daytona International Speedway and 400 Florida homes per year, according to officials of the speedway and Florida Power & Light. The FPL Solar Pavilion and FPL Solar Patio project at the speedway will be in the Midway, the Sprint FANZONE and Lot 10 parking area. [Bay News 9]
¶ Procter & Gamble signed a partnership with EDF Renewable Energy to build a wind farm in Texas. It will generate 370,000 MWh of electricity per year, enough to meet the electricity needs for all Procter & Gamble North American Fabric & Home Care plants, where Tide, Cascade, and other such products are produced. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Customers of Xcel Energy Inc in Minnesota will have the option of signing long-term deals to get their electricity from wind and solar farms under a proposed program. The program, which requires state regulatory approval, would be open to all customers. But key features are aimed to support corporate sustainability targets. [Minneapolis Star Tribune]
¶ Two weeks after a developer came to town to disclose details of what would be Vermont’s largest wind-turbine site, the project’s opponents presented an impassioned case against building any wind farms in Stiles Brook Forest. Opponents to the proposal painted a picture of troubles, at a meeting they organized. [vtdigger.org]
¶ Hillary Clinton outlined a $30 billion plan to help communities and individuals that rely on coal to recover from the industry’s decline. Clinton has said repeatedly she will not forget the coal workers who “kept the lights on” and drove economic growth. Her campaign said the plan fits squarely with her climate priorities. [Rapid News Network]
¶ The New York Department of State has objected to relicensing the Indian Point nuclear plant on the Hudson River, saying it kills millions of fish larvae and sits near seismic faults with an earthquake threat to millions of people. It says the plant is incompatible with the safety of New York City 24 miles downstream. [Albany Times Union]
Early October 2015
World:
¶ Electricity sent to the National Grid by wind turbines in Scotland was 82% higher in September than the same month last year, analysis by WWF Scotland and data company WeatherEnergy found. The grid took 563,835 MWh of power from Scotland’s windfarms in September 2015, up from 308,301 MWh in September 2014. [Scotsman]
¶ Australia’s first wind farm commissioner has been appointed to take office for three years. The government also established a scientific panel to “provide advice on the science and monitoring of potential impacts of wind turbine sound on health and the environment,” as part of a deal with anti-wind farm crossbench senators. [Sydney Morning Herald]
¶ The Indian Government is likely to overachieve its 2030 climate intensity target without having to implement any new policies, according to Climate Action Tracker. In its UN climate plan, India has stated it would reduce the emissions intensity of its economy by 33–35% below 2005 levels by 2030. [Business Spectator]
¶ SunEdison, one of the world’s biggest renewable energy investors has warned that “draconian” UK subsidy cuts will kill solar power in Britain, blaming policy changes for a pullback that led to the collapse of a big installer and nearly 1,000 job losses. Just two weeks ago Drax said it was pulling out of a £1 billion UK plan. [Financial Times]
¶ Denmark’s renewable cumulative capacity is expected to reach 16.1 GW by 2025, up from 13.5 GW in 2014. The country is expected to produce 75% of its electricity from renewables, with wind energy the major resource. Wind power is forecast to account for 44.8% of total power generation by 2020. [Energy Live News – Energy Made Easy]
US:
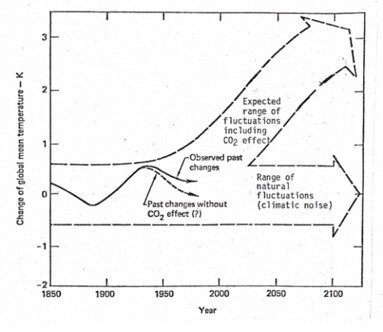
This is a graph from the now famous Exxon documents that date to 1981, explaining how Exxon scientists were projecting global warming with continued release of the greenhouse gas CO2 into the atmosphere.
¶ America’s reliance on renewable sources of energy has reached historic levels and is poised to make even greater gains in the near future, according to report by the Natural Resources Defense Council. The report found that energy sector carbon pollution was lower last year than in 1996, down 10% reduction in the past decade. [solarserver.com]
¶ DC Water commissioned a $470 million project that produces 10 MW of green electricity from wastewater treatment. The project includes a dewatering building, 32 sleek thermal hydrolysis vessels, four concrete anaerobic digesters holding 3.8 million gallons of solids each, and three turbines the size of jet engines. [Power Technology]
A simple electric solution for the United States Postal Service costs less than 5 billion dollars

The Tripl is a two-in-front electric trike with a perfectly reasonable top speed of 28mph. It's about eight feet long and four feet wide, and it weighs 664lbs empty. A hub-mounted electric motor drives the rear wheel, and the narrow front wheels are set up to allow a London Taxi-like 25ft turning radius. And unlike its pedal-powered cargo-carrying rivals, the Tripl has a reverse switch. After an eight-hour charge (4.5 hours with the optional quick charger) it has range of 60 miles, enough for a full day’s delivery in an urban core.

The design not just better for cities, it’s better for citizens. Running boards on either side of the back wheel, coupled with an adjustable seat, allow the driver to simply step up on to the saddle. There’s no need to throw a leg over a bar, and throw out a back in the process.

The front of the vehicle also has low ground clearance. While this had advantages, there were trade offs. The vehicle was tested successfully in warmer climates, but when actually used in places with substantial snow fall, they became difficult to control and were poorly adapted to those conditions.
Recently it was announced that General Motors was actively pursuing this new contract, which would have them provide the USPS with 180,000 new vehicles at a cost of at least $5 billion
September 2015
Science and Technology:
¶ Toyota now collects more than 90% of the nickel-metal hydride batteries used in its hybrid cars, and is aiming for 100% collected. But what happens to the batteries after they’re collected? Some are recycled, but from an environmental perspective, it’s even better if they are reused. They have a second life in Yellowstone Park. [The Guardian]

Reused Toyota Camry Hybrid battery packs store solar energy in a distributed energy system now online at the Lamar Buffalo Ranch field campus in the Yellowstone National Park. Photograph: Toyota
¶ A new line of solar modules from JA Solar eliminates the need for racking, allowing for direct mounting on rooftops, cutting installation time. The modules are made up of 60 “cell laminates” per unit, surrounded by a heavy-duty aluminum frame strong enough for them to be mounted directly to the roof, without any additional racking. [CleanTechnica]
World:
¶ India’s National Thermal Power Corporation had invited bids last May for ten separate 50-MW solar PV projects to be developed in phases in the Ghani Solar Park, Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh. Bids were submitted last week, and the call has been oversubscribed by 10 times, with a total of 30 developers in the foray. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Utility-scale grid connected battery storage may reach 12 GW by 2024, while annual revenues could grow to $8.44 billion, according to a report from Frost & Sullivan. The US will be a leader, followed by China, Japan and Germany. Despite an overall positive outlook, there are significant market challenges to overcome. [pv magazine]
¶ The mayor of London, reminded cabinet ministers that 10,000 local jobs were dependent on this renewable power technology which had, in his view, “many, many attractions”. The warning from the high-profile Conservative came as the chief executive of Shell predicted solar would become the “backbone” of our energy system. [The Guardian]

Solar panels on residential houses in East Dulwich, Southwark, South London. Photograph: Alamy
¶ Australia will be one of the first countries to get Tesla’s vaunted Powerwall battery storage system. Several companies are scrambling to sign up Australian households with solar rooftops. Tesla said that its 7-kWh home energy storage units, predicted to arrive in Australia in 2016, would be available by the end of the year. [The Guardian]
¶ With Canada’s federal government out for the count, it was the provinces who spearheaded the addition of a total 3.63 GW in renewable power generation in 2014 and a rate of investment in green energy that was 88% higher than in 2013, pushing Canada to sixth place ranking for renewables development, Clean Energy Canada says. [National Observer]
US:
¶ The Department of Transportation in Washington wrapped up a bid proposal for up to 800 electric buses in 12 different categories. BYD buses has been awarded the contract in 10 of those categories. The contract may be the biggest in US history. It includes buses from 30 to 60 feet in length for highway and intra-city applications. [CleanTechnica]

Electric bus. BYD photo.
¶ New solar energy funding has been announced along with a new DOE energy efficiency roadmap that aims to double energy efficiency in the US by 2030 through standards for utilities, vehicles, and consumer goods. Solar energy is already cost competitive in 14 US states. This may make it competitive in the rest of them. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Two extensive studies reveal that major US business identities have knowingly undermined the health, safety, and survival of real humans and other living things in regards to climate. One examines ExxonMobil’s actions, and the other implicates almost half the world’s 100 largest companies in obstructing climate change legislation. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Officials at the Pilgrim Nuclear Power Station are considering whether they can afford the multimillion-dollar safety improvements and other reforms required by federal officials. If not, they say, they might close the plant. The NRC downgraded the plant’s safety rating this month, listing Pilgrim as among the least safe in the country. [The Boston Globe]

The Pilgrim nuclear power plant in Plymouth, Massachusetts. David L. Ryan / Globe Staff / File
¶ Sulphur Springs Valley Electric Cooperative and SunPower announced signing a 20-year power purchase agreement. SunPower will build a 20-MW solar PV plant in Cochise County, Arizona. Expected to be operational by the end of 2016, the plant should provide enough electricity for 4,500 homes, on an annual basis. [Your Renewable News]
¶ The mayor of Burlington, Vermont, and the president of the University of Vermont announced a partnership between the city and UVM develop 1 MW of solar energy projects on UVM campus properties. A request for proposals encourages a wide variety of projects, including roof-top installations and solar canopies over parking areas. [vtdigger.org]
¶ SunEdison announced it is supplying lithium-ion batteries for nine prototype homes in California that will be fully powered by renewable energy. The zero-net energy home project is part of a larger state-wide plan to have all new construction homes run 100% off renewables, such as photovoltaic roof panels, by 2020. [Computerworld]
August 2015
World:

¶ Solar and onshore wind are supported by 76% and 59% of Brits, respectively, a survey commissioned by UK renewable power supplier Good Energy Group Plc says. The findings were published after the Department of Energy and Climate Change released its latest attitudes tracker, which omitted questions about support for specific renewable technologies. [SeeNews Renewables]
US:
¶ Mary Nichols, the chair of the California Air Resources Board, said she hopes to implement new rules in the state that would eventually prohibit the sale of new cars that are equipped with internal combustion engines. The zero-emissions vehicle program California now has in place requires that 2.7% of new cars purchased in the state in 2015 be free of greenhouse gas emissions. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Adding to a hydropower bill that he already laid before the Legislature, Massachusetts Governor Charlie Baker has filed a bill to accelerate solar power industry growth in Massachusetts and then adjust incentives. The administration says its bill will help the state meet “well ahead of schedule” its goal of 1,600 MW of solar power by 2020, while lowering costs. [Wicked Local Brookline]
¶ California Governor Jerry Brown signed a bill Friday that allows BART [the rapid transit system in the San Francisco Bay area] to purchase renewable energy directly from wholesale suppliers as the rail system looks to further reduce its carbon footprint. Under the new law, BART officials would no longer have to go through a third party to buy renewable energy on their behalf. [SFGate]
¶ Southern California has missed a long-standing federal deadline to reduce toxic soot and other small particle air pollution because unhealthful levels of such pollutants persist in northwest Riverside County. The Bush administration set rules for communities in Southern California’s ocean-to-mountains air basin to meet the goal by 2015. The standard has been missed, however. [Press-Enterprise]
¶ One of the Vermont’s most prominent renewable energy developers is proposing to build more wind power in a region of Vermont that has been divided over such projects for years. David Blittersdorf wants to erect two wind turbines on a Northeast Kingdom ridgeline in the 1,100-person town of Irasburg and produce enough electricity to power more than 2,000 homes. [vtdigger.org]
July 2015
Science and Technology:

Polar bear. Photo by Ansgar Walk.
World:
¶ The Japanese government says the country will cut 26% of their greenhouse gas emissions from 2013 levels by 2030. They will submit the plan to the UN for the global summit on climate change in Paris in November. The plan calls for relying slightly less on nuclear power than on renewable energy. [The Japan Times]
¶ Global investment in new nuclear is an order of magnitude less than renewable energy investment. That is just one finding of a new independent report on the state of the worldwide nuclear industry that issued on Thursday. No matter how you look at the nuclear industry, the picture isn’t pretty. [Greentech Media]
¶ A Japanese delegation from Fukushima, site of a nuclear disaster in March 2011, visited Switzerland to discuss energy policies, technologies and the development of renewable forms of energy. Almost five years after the Fukushima Disaster, many inhabitants of the prefecture can’t lead normal lives. [swissinfo.ch]
¶ The first house in the UK that produces more energy than it consumes has been built in Wales by Cardiff University researchers. The prototype house combines renewable energy with multiple approaches to energy efficiency, including layers insulation, and energy-efficient windows and doors. [E&T magazine]
US:
¶ An Analysis Group report claims the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative involving 9 New England and Mid-Atlantic states has added $1.3 billion in economic activity to the region since 2011 and reduced carbon emissions by 15%. The program has also saved people in the area $460 on electricity. [CleanTechnica]
¶ Santa Monica’s Big Blue Bus, a municipal bus operator in the Westside region of Los Angeles, is one of the first municipal transit authorities in the US to convert its fleet to biomethane, which is rated 90% cleaner than diesel. Fuel supplier Clean Energy Fuels call the product “renewable natural gas.” [NGV Global]
¶ The NY Prize Microgrid Competition is a first-in-the nation $40 million competition to help communities in New York State create their own microgrids. More than 130 proposals were submitted statewide. The town of Ossining is one winner, and will receive $100,000 to complete a feasibility assessment. [Patch.com]
¶ In a deal expected to save residents $45 million over the next two decades, Washington, DC, Mayor Muriel Bowser said the city has signed a power purchase agreement with Iberdrola for the entire output of a wind farm in Pennsylvania. The total purchased will be about 125,000 MWh each year. [Utility Dive]
March 2015
World:
¶ According to a study by the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems, the cost of producing power in central and southern Europe will have declined to between 4 and 6 cents per kWh by 2025, and to as low as 2 to 4 cents by 2050.” The study was commissioned by the think tank Agora Energiewende. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The UK low carbon economy was worth £122 billion in 2013 and has been growing at 7% per year, according to government figures. A low carbon investment report from the Department of Energy and Climate Change says the sector supports over 460,000 jobs, or about 1.5% of all UK jobs. [Business Green]

¶ A new report published by Australia’s Climate Council has shown just how dramatically Australia is falling behind other leading world economies in renewable energy generation. The failure is due to the current policy uncertainty resulting from the government’s review of the Renewable Energy Target. [CleanTechnica]
¶ EDF Energy has agreed to buy the electricity generated from 104-MW of solar farms in the UK, owned by Primrose Solar. The 15-year power purchase provides for an inflation-linked guaranteed minimum price. The price floor enhances Primrose Solar’s ability to raise capital against the projects. [Clean Technology Business Review]
¶ Gas fueled power plants will soon supply all the electricity in Beijing as China strives to cut down pollution levels there. The last of four coal-fired power plants, an 845-MW plant of China Huaneng Group Corp, is scheduled to be closed in 2016. The gas plants will have double the capacity of the old plants. [India Gazette]
¶ More than a million homes in the UK could be heated using green technology that takes heat from nearby rivers and canals and pumps it into the home. The Energy Secretary is promoting water-source heat pumps, taking heat from 4041 rivers, estuaries, coastal sites and canals the government has identified. [The Independent]
US:
¶ A proposal to build a hydroelectric power plant in the San Vicente Reservoir near Lakeside is going before the San Diego City Council’s Environment Committee. The project would require construction of an upper reservoir that would pour into the existing body of water. The plant would produce 500 MW. [Times of San Diego]
¶ A Colorado company, Red Rock Biofuels, is planning a $200 million biofuels refinery in Lakeview, Oregon where it will refine jet fuel to be used by Southwest Airlines. The refinery will also produce diesel and naphtha fuel from its wood pulp stock through wood gasification and Fischer-Tropsch catalysis. [CleanTechnica]
¶ The US DOE reported that California is the first state to get 5% of its electricity from large-scale solar power installations. In 2014, solar power plants in California generated 9.9 million MWh, more than all other states combined. The report does not count rooftop systems, which are a large part of the total. [SFGate]
¶ SunPower Corp will build the 15-MW solar array on Nellis Air Force Base in Nevada. The $50 million plant will be owned by NV Energy on land leased from the Air Force in the southwest part of the base. Together with an older 13.2-MW solar plant, it will power all base facilities during daylight hours. [Las Vegas Review-Journal]
¶ Carbon Tracker’s report, “The US Coal Crash,” argues that coal demand is in a structural decline that could also befall oil and gas producers world over in coming years. Companies that fail to adapt to technological and policy changes that will ultimately curb greenhouse-gas emissions could lose billions. [Bloomberg]
¶ A measure reducing the amount of renewable energy sources utilities would have to tap to provide electricity for their customers by 2020 has narrowly passed the New Mexico House and is heading to the senate. The current standard increased from 10% to 15% this year and requires 20% in 2020. [PennEnergy]
¶ Enel Green Power has commenced the construction of a new wind farm in Oklahoma. The company plans to invest approximately $130 million to construct the Little Elk wind project, which will have a total installed capacity of 74 MW. The wind farm will generate enough power for 27,000 US homes. [Greentech Lead]
¶ The California Public Utilities Commission failed to probe possible Southern California Edison responsibility for design errors that led the demise of the San Onofre nuclear power plant. Now a California Assembly Committee is asking the commission for review the $4.7 billion San Onofre settlement. [CleanTechnica]